what is virus ?
virus is a latin word it means poison . virus is a smallest microorganism it not seen in simple microscopy. its appear in light microscopy or ultramicroscopy. the size of virus is 20 - 300 nm. it mostly found in a human body cells and virus are mostly grow in human cells so we are normally called virus is a intracellular organism. the study of virus also called virology virus of measured in nanometer.
definition of virus-
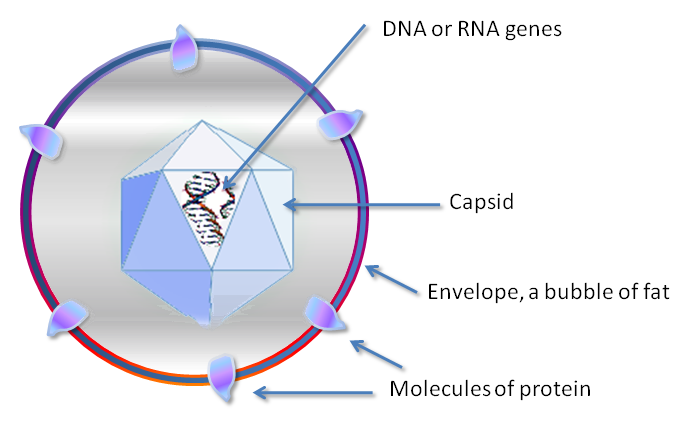
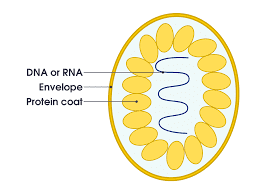
virus is a smallest infectious agent they are replicated only in a living cells and virus are consist of DNA or RNA but it is never made of both acid . such as DNA virus and RNA virus .
General character of virus -
REPLICATION OF VIRUS -
the replication of virus is divided into six steps -
2. penetration - it is a second step of replication of virus in this step virus capsid is injected in the host cell. the entry is achieved through membrane fusion, pilus reaction, ejection, permeabilization.can occur by a cellular mechanism called receptor mediated endocytosis, it can involve the fusion of the virus envelope with the plasma membrane of host cell.
3. uncoating - in this step after penetration of the host cell virus remove their virus capsid and virus are unmask the nucleic acid inside and all process of this we are called uncoating and again this process viral capsid is removed and release the virus nucleic acid into the host cell.resulting in a loss of virion infectivity.
4. biosynthesis - in this step after uncoating the viral nucleic acid direct the bio-synthetic machinery of host cell stop the normal cellar metabolism and produced its own viral components.
5. virion assembly - in this step newly synthesized nucleic acid and protein are assembled from new virus particles this may take place in nucleic . assembly of various viral components in to complete virus particle.the formation of inclusion body.
6. Release - it is a last step of replication in this step the release mature virion from their host cell. the new virion are able to infect adjacent cell and repeat the replication again.
FACTOR AFFECTING OF VIRUS
the virus is very sensitive against environmental factor to compared other organism. temperature, PH,mostly affect their infectious capacity. mostly some factor are affect the virus life cycle
2. PH - PH is a good condition for virus to living.virus are fastly grow in human body PH
some imbalance in HP virus are loss their infectious capacity .
3. lipid solvent - ether , chloroform or any other lipid solvent kill the viruses. virus dies when come with contact of lipid solvent .
more topic are available on this blog related to bsc nursing go on blog home and seen right side and search what you want
https://nursinglectureclass.blogspot.in/2017/12/factor-affecting-bacterial-growth-and.html
General character of virus -
- virus are the smallest infective agents
- they are obligated parasites
- they multiply only in living cell and using host cell
- virus cannot make energy
- virus is never made both DNA and RNA
- virus can easily crystallized
- virus are non-cellar organism
- its easily transmitted
- virus have no metabolic activity
REPLICATION OF VIRUS -
the replication of virus is divided into six steps -
- adsorption
- penetration
- uncoating
- biosynthesis
- virion assembly
- release
2. penetration - it is a second step of replication of virus in this step virus capsid is injected in the host cell. the entry is achieved through membrane fusion, pilus reaction, ejection, permeabilization.can occur by a cellular mechanism called receptor mediated endocytosis, it can involve the fusion of the virus envelope with the plasma membrane of host cell.
3. uncoating - in this step after penetration of the host cell virus remove their virus capsid and virus are unmask the nucleic acid inside and all process of this we are called uncoating and again this process viral capsid is removed and release the virus nucleic acid into the host cell.resulting in a loss of virion infectivity.
4. biosynthesis - in this step after uncoating the viral nucleic acid direct the bio-synthetic machinery of host cell stop the normal cellar metabolism and produced its own viral components.
5. virion assembly - in this step newly synthesized nucleic acid and protein are assembled from new virus particles this may take place in nucleic . assembly of various viral components in to complete virus particle.the formation of inclusion body.
6. Release - it is a last step of replication in this step the release mature virion from their host cell. the new virion are able to infect adjacent cell and repeat the replication again.
FACTOR AFFECTING OF VIRUS
the virus is very sensitive against environmental factor to compared other organism. temperature, PH,mostly affect their infectious capacity. mostly some factor are affect the virus life cycle
- temperature
- PH
- lipid solvent
2. PH - PH is a good condition for virus to living.virus are fastly grow in human body PH
some imbalance in HP virus are loss their infectious capacity .
3. lipid solvent - ether , chloroform or any other lipid solvent kill the viruses. virus dies when come with contact of lipid solvent .
disease caused by virus - different type of virus present in environment they are capable to cause disease in human 1
1.hepatitis disease cause by virus hepatitis A,B,C,D, and E virus cause hepatitis in human. in hepatitis disease hepatitis virus mainly affect on the liver.
2. lassa virus, it is responsible for causing lassa fever in human the common symptom of lassa fever muscle pain, weakness, vomiting , and less commonly bedding from mouth and gastrointestinal tract.
3. measles virus is a single cell RNA virus it is responsible for causing respiratory disease such as runny nose, cough , fever, sneezing and red eyes. it is spread by direct contact with infected person, infected person .
4. mumps virus,virus is the causative agent of mumps it is commonly caused in childhood characterized by swelling of salivary gland parotid gland mumps virus transmitted by direct contact.
more virus are present in environment for more information search on www.wikipedia.com
laboratory diagnosis of viral infection -
specimen - specimen should be collected from patient , preserved and transported to the laboratory in the proper manner.laboratory diagnosis of viral infections can be carried out by the following methods
1. cytological examination - the cytologic examination of specimens provides a rapid inintial diagnosis for viral infection .
2. direct detection of virus
a. light microscopy - demonstration of the inclusion body is a routine diagnostic method. rabies may be detected by light microscopy
b. electron microscopy - clinical applications of electron microscopy include detection of rotvavirus and hepatitis A virus in fecal specimen.
c. microelectronic microscopy - this method use to detection of electric virus such as rotavirus .
3. virus isolation
4. detection of virus protein
5. serological test
more topic are available on this blog related to bsc nursing go on blog home and seen right side and search what you want








0 comments:
Note: only a member of this blog may post a comment.