ANTIGEN ANTIBODY REACTION
INTRODUCTION -
the antigen antibody reaction process is start after invasion of antigen in our body. antigen enters in human body and human immune system take action imminently and produced antibody against antigen in other word we are say immune system produced resistance against pathogen or antigen. the body immune system produced antibody and start reaction.antigen -antibody reaction is widely used in laboratory diagnosis,including immunohaematology(immunohaematology know as blood banking is a branch of hematology which studies antigen - antibody reactions).antigen antibody reaction based on the hormonal immunity or antibody.
What is antigen
a toxic or other foreign substance that stimulate an immune response in the body especially the production of antibodies or an antigen is the foreign particle enter in human body and stimulate antibody immune response. an antigen is a molecule capable of inducing an immune response in the host organism. it is harmful for our body. antigen mainly microorganism such as virus,bacteria,fungi and parasites. they also come from envelopment. antigen are capable for causes infection in human body.antigen is a foreign particles usually proteins which is capable of generating immune response in the body.
definition of antigen -
"antigen is define as any substance that can stimulate the production of antibodies that is called antigen."
"antigen are invaders that sneak into our body and can possibly cause us infection or harm and stimulate production of antibodies."
"any substance that capable to stimulating immune reaction that is called antigen such as virus,bacteria,fungi,parasite etc."
types of antigen
any substance come from environment like microorganism,dust particle,blood cells of other person and transplanted organs and tissues all are antigen in some case medicine and food also act as antigen. antigen commonly divided in to two types they are discussed blow
what is antibody
antibody is the capable for protection of antigen and its take immediate action against antigen.antibody is a host protein (immunoglobulin) produced response to presence of antigen or other foreign particle in the body. antibody or immunoglobulin is a Y- shape protein that are produced by plasma cells that is used by immune system to kill pathogen such as bacteria and viruses. antibody is Y shaped immunoglobulin(Ig) that are produced by the immune system to neutralized pathogen or antigen. antibody is a army of our body. antibody are as specialized serum protein which response to antigen stimulate. they specially react with the antigen which stimulate their production.
definition of antibody -
" antibody is know as protein that mainly produced by plasma cell that is used by immune system to kill pathogen such as microorganism (bacteria,virus, protozoa,fungi,parasite)"
" blood protein produced in response to and counteracting a specific antigen.in other word antibody is the army of our body."
" any substance produced by the body in response to an foreign particle or antigen are called antibodies."
structure of antibodies(immunoglobulin) -
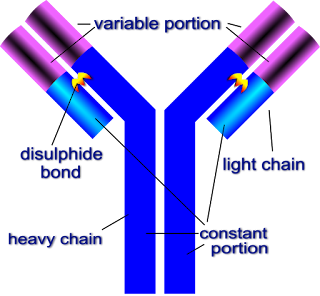
antibodies is a defense system of human body they take action against antigen each antibody attache with the specific antigen. antibodies play essential role in immune system.antibody is also known as immunoglobulin, each immunoglobulin consist of four polypeptide chain two heavy chain and two light chain and polypeptide chain held together by disulfide bond. to chain are smaller in size are called light chain and other two chain are large in size are called heavy chain.
light chain - each light chain is made up of 214 amino acid residues and each light chain has two regions variable and constant.
heavy chain - heavy chain are present in five different types. heavy chain is gamma(ሃ), mu(μ), alpha (α), delta (ઠ), epsilon (ε). antibody consist of heavy chain and heavy chain made up of 450 amino acid. it consist of to part variable and constant.
fab ligament - its Y shaped molecule bind to the antigen. each fab consist of anino acid
classes of antibody - five different types of immunoglobulin present in human blood these are immunoglobulin G (Ig), immunoglobulin M (IgM), immunoglobulin A (IgA) , immunoglobulin D (IgD) , immunoglobulin E (IgE).
antigen and antibody reaction -
any antigen enter into the human body and human body take action against antigen. antibody attach with the antigen these process is called antigen antibody reaction. antigen antibody reaction is a chemical reaction between antibodies produced by the b cell of the white blood cell during immune reaction.antibody protect from the foreign particle such as toxin and pathogen in blood.antigen antibody reaction is very specific. it is useful to identify pathogen in human blood and its help to diagnosis of varies disease.
an+ ab ⇌ an -ab complex
types of antigen - antibody reaction -
b. detection of bacteria
2. agglutination reaction. -
agglutination reaction is the process of a particular antigen is mixed with is corresponding antibody this process is called isogglutinin . (the term isogglutinin commonly used in blood grouping its means clumping example bacteria cell and red blood cell). in agglutination reaction antigen mixed with antibody in presence of electrolyte at the suitable temperature and ph the particle are agglutinated or clumped.
a) slide agglutination - slide agglutination is the repaid method to determine clumped
antibodies .
3. ELISA -
ELISA is a technique to use the detect antigen and antibody in sample Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay is the antigen antibody reaction test we are use this test in antibody color change and identify substance.
4. immunofluorescence reaction -
it is a technique to use in laboratory to determine location of antigen in a tissue by reaction with antibody or antigen.
5. complement fixation -
complement fixation test is a traditional test. this test mostly used to determine presence of specific antigen or antibody in a sample.example bacteria requirement some non specific unstable component of fresh serum which are called complement reaction.
What is antigen
a toxic or other foreign substance that stimulate an immune response in the body especially the production of antibodies or an antigen is the foreign particle enter in human body and stimulate antibody immune response. an antigen is a molecule capable of inducing an immune response in the host organism. it is harmful for our body. antigen mainly microorganism such as virus,bacteria,fungi and parasites. they also come from envelopment. antigen are capable for causes infection in human body.antigen is a foreign particles usually proteins which is capable of generating immune response in the body.
- antigen is foreign substance
- antigen stimulate immune response
- antigen is a invaders such as bacteria,virus,fungi etc.
- it come from environment.
- its caused infection or harm for our body
- antigen is a foreign particles usually protein which is capable of stimulating immune response.
- antigen is a molecules capable of inducing an immune response
definition of antigen -
"antigen is define as any substance that can stimulate the production of antibodies that is called antigen."
"antigen are invaders that sneak into our body and can possibly cause us infection or harm and stimulate production of antibodies."
"any substance that capable to stimulating immune reaction that is called antigen such as virus,bacteria,fungi,parasite etc."
types of antigen
any substance come from environment like microorganism,dust particle,blood cells of other person and transplanted organs and tissues all are antigen in some case medicine and food also act as antigen. antigen commonly divided in to two types they are discussed blow
- complete antigen
- incomplete antigen
- complete antigen - complete antigen is able to stimulate antibody formation and produced a specific and observable reaction with immunoglobulin(antibody). complete antigen composed of the macro molecular carrier and epitopes that cane induce immune response.
- incomplete antigen - a antigen capable of reacting with a specific antibody but unable to induce the formation of antibody they are unless bound with other molecules. its also called partial or incomplete protein.
- foreignness - antigen must be foreign substance because body show immune response against foreign antigen only.
- size - the most active antigen have molecular mass of something 1400 to 6,00,00. large molecules highly antigenic and small molecules less antigenic.example tetanus toxioid
- chemical nature - antigen are mainly protein, protein are more effective antigen as compere to carbohydrates because protein are able to induce antibody production .
- organ specificity - some antigen are organ and they are confined to that specific organ.
- species specificity - tissue of all individual in a species process specific antigen, human blood protein can be different from animal blood protein by specific antigen - antibody reaction
- iso - specificity - antigen found in some but not all member of species. individual in a species are grouped according to the presence of different autoantigenens. blood grouping in human is done depending upon the erythrocyte of antigen.
- auto specificity - the self antigen are ordinarily not immunogenic but certain condition circumstances less protein other may be act as autoantigens.
- heterophiles - its show by hetrophils antigens. some closely related antigens occurring in different biological species , kingdoms and class are also known as hemetrogenetic .
what is antibody
antibody is the capable for protection of antigen and its take immediate action against antigen.antibody is a host protein (immunoglobulin) produced response to presence of antigen or other foreign particle in the body. antibody or immunoglobulin is a Y- shape protein that are produced by plasma cells that is used by immune system to kill pathogen such as bacteria and viruses. antibody is Y shaped immunoglobulin(Ig) that are produced by the immune system to neutralized pathogen or antigen. antibody is a army of our body. antibody are as specialized serum protein which response to antigen stimulate. they specially react with the antigen which stimulate their production.
- antibody is the army of human body
- they are capable to fight against antigen or any foreign particle
- antibody is a host protein
- they are present in the Y shape
- antibodies also know as immunoglobulin
- antibody consist of polypeptides
definition of antibody -
" antibody is know as protein that mainly produced by plasma cell that is used by immune system to kill pathogen such as microorganism (bacteria,virus, protozoa,fungi,parasite)"
" blood protein produced in response to and counteracting a specific antigen.in other word antibody is the army of our body."
" any substance produced by the body in response to an foreign particle or antigen are called antibodies."
structure of antibodies(immunoglobulin) -
antibodies is a defense system of human body they take action against antigen each antibody attache with the specific antigen. antibodies play essential role in immune system.antibody is also known as immunoglobulin, each immunoglobulin consist of four polypeptide chain two heavy chain and two light chain and polypeptide chain held together by disulfide bond. to chain are smaller in size are called light chain and other two chain are large in size are called heavy chain.
light chain - each light chain is made up of 214 amino acid residues and each light chain has two regions variable and constant.
heavy chain - heavy chain are present in five different types. heavy chain is gamma(ሃ), mu(μ), alpha (α), delta (ઠ), epsilon (ε). antibody consist of heavy chain and heavy chain made up of 450 amino acid. it consist of to part variable and constant.
fab ligament - its Y shaped molecule bind to the antigen. each fab consist of anino acid
classes of antibody - five different types of immunoglobulin present in human blood these are immunoglobulin G (Ig), immunoglobulin M (IgM), immunoglobulin A (IgA) , immunoglobulin D (IgD) , immunoglobulin E (IgE).
antigen and antibody reaction -
any antigen enter into the human body and human body take action against antigen. antibody attach with the antigen these process is called antigen antibody reaction. antigen antibody reaction is a chemical reaction between antibodies produced by the b cell of the white blood cell during immune reaction.antibody protect from the foreign particle such as toxin and pathogen in blood.antigen antibody reaction is very specific. it is useful to identify pathogen in human blood and its help to diagnosis of varies disease.
an+ ab ⇌ an -ab complex
types of antigen - antibody reaction -
- precipitation reaction.
- agglutination reaction.
- ELISA.
- immunofluorescence reaction.
- complement fixation.
- precipitation reaction. - in a soluble antigen combines with the antibody in the presence of electrolyte at the particular temperature and ph. the antibody causing precipitation is called precipitin. antigen antibody reaction is called precipitation reaction.
a. standardization of toxins and antitoxin
b. detection of bacteria
c. demonstration of antibody in serum
agglutination reaction is the process of a particular antigen is mixed with is corresponding antibody this process is called isogglutinin . (the term isogglutinin commonly used in blood grouping its means clumping example bacteria cell and red blood cell). in agglutination reaction antigen mixed with antibody in presence of electrolyte at the suitable temperature and ph the particle are agglutinated or clumped.
a) slide agglutination - slide agglutination is the repaid method to determine clumped
antibodies .
3. ELISA -
ELISA is a technique to use the detect antigen and antibody in sample Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay is the antigen antibody reaction test we are use this test in antibody color change and identify substance.
4. immunofluorescence reaction -
it is a technique to use in laboratory to determine location of antigen in a tissue by reaction with antibody or antigen.
5. complement fixation -
complement fixation test is a traditional test. this test mostly used to determine presence of specific antigen or antibody in a sample.example bacteria requirement some non specific unstable component of fresh serum which are called complement reaction.









Very Helpful Article. This Is Really Useful And Interesting Post .
ReplyDeleteHealth Care Product